How to Create an Effective Information Security Policy for Your Company
In this digital era, businesses face increasing threats to their information assets. With data breaches, cyberattacks, and insider threats happening, it’s become important to protect sensitive information. An effective information security policy provides a structured framework to safeguard data, define responsibilities, and maintain regulatory compliance.
In this blog, we’ll explain how companies in Bangalore can create robust information security policies tailored to their unique needs.
Understanding Information Security Policy
An information security policy is a formal document outlining how an organization manages, protects, and distributes information. It sets the rules, roles, and responsibilities for employees and stakeholders while establishing the procedures to protect digital and physical information assets. In India, companies handling sensitive data must also comply with regulations such as the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000, and the recent amendments in data privacy and cybersecurity guidelines.
A comprehensive information security policy helps businesses:
- Protect confidential company and client data.
- Prevent financial losses caused by cyber incidents.
- Comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Build trust with clients and business partners.
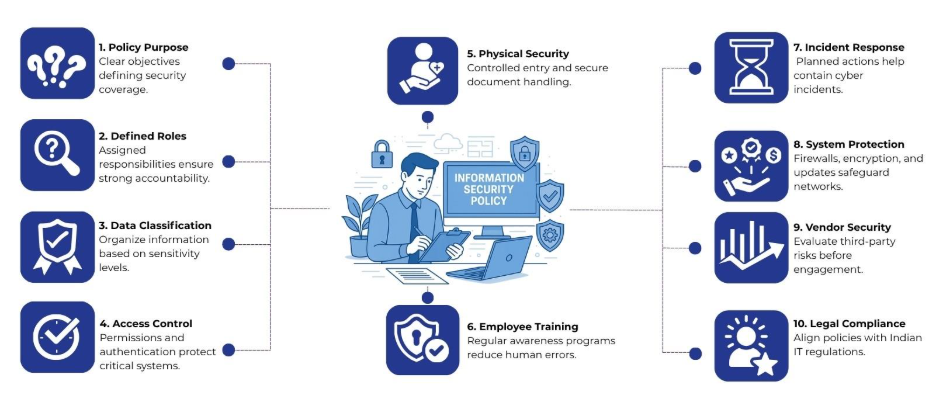
Key Components of an Effective Information Security Policy
A successful information security policy is more than a list of rules; it serves as a strategic tool to safeguard information. Companies in Bangalore should focus on the following elements:
1. Purpose and Scope
Define the objective of the policy clearly. Explain why information security is important for your organization and identify the information systems, assets, and business processes covered. The scope should include:
- Employee and contractor access to systems.
- Handling customer and financial data.
- Cloud storage and third-party software usage.
- Physical and digital data storage.
A clear scope prevents ambiguity and clarifies which areas the policy applies to, including remote work scenarios.
2. Roles and Responsibilities
Assign specific roles and responsibilities for managing information security. For example:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or IT head: Manages the policy implementation and monitors compliance.
- Department Heads: Maintain security standards within their teams.
- Employees and Contractors: Follow security practices, report incidents, and protect credentials.
Clearly defining responsibilities avoids confusion and strengthens accountability.
3. Data Classification and Handling
Classify information based on sensitivity:
- Public: Can be shared externally without restrictions.
- Internal: Limited to employees and internal stakeholders.
- Confidential: Requires restricted access and protection.
- Highly Confidential: Access only to authorized personnel with strict handling procedures.
Companies in Bangalore, particularly those in IT, finance, or healthcare sectors, must comply with data privacy regulations when handling customer or patient information. Similarly, employees should follow guidelines for storing, sharing, and disposing of classified data.
4. Access Control
Access control policies determine who can view, modify, or delete information. Key practices include:
- Role-based access privileges for employees.
- Multi-factor authentication for sensitive systems.
- Periodic review and revocation of access for inactive accounts or terminated employees.
Implementing access control reduces the risk of unauthorized access, one of the most common causes of data breaches in organizations.
5. Physical Security Measures
Protecting physical information assets is as important as digital security. Include measures such as:
- Secure office entry with ID badges.
- Restricted access to server rooms and data centers.
- CCTV monitoring of sensitive areas.
- Secure storage and disposal of physical documents.
Many businesses overlook physical security, making it a weak point in overall information security management.
6. Security Awareness and Training
Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. That’s why regular training programs help employees recognize phishing attempts, malware attacks, and social engineering. Focus on:
- Safe use of company devices and networks.
- Recognizing suspicious emails and links.
- Reporting potential security incidents promptly.
Startups and SMEs in Bangalore can benefit significantly from building a culture of information security awareness.
7. Incident Management
Prepare a structured approach for responding to security incidents. This includes:
- Defining what constitutes an incident (e.g., data breach, malware infection, insider threat).
- Creating an incident response team.
- Documenting reporting procedures and escalation paths.
- Performing post-incident analysis to prevent recurrence.
Indian regulations, such as the IT Act and CERT-In guidelines, require prompt reporting of cybersecurity incidents in certain cases. A clear incident management plan helps businesses comply with these regulations.
8. Network and System Security
Protecting digital infrastructure is critical. Include policies for:
- Firewall and antivirus usage.
- Secure Wi-Fi and VPN connections for remote work.
- Regular software updates and patch management.
- Encryption of sensitive data during transmission and storage.
Indian IT regulations increasingly demand robust security measures for organizations handling personal or financial information.
9. Third-Party Vendor Security
Many companies rely on external vendors for services like cloud storage, payment processing, or software development. A policy should cover:
- Vendor security assessment before engagement.
- Data protection requirements in contracts.
- Periodic security audits of vendor systems.
Third-party breaches have become a significant source of data compromise, making vendor management critical for comprehensive information security.
10. Compliance and Legal Considerations
Businesses in Bangalore must align their policies with national regulations and international standards, including:
- Information Technology Act, 2000: Governs data protection, cybersecurity offenses, and digital transactions.
- CERT-In Guidelines: Provides standards for incident reporting and cybersecurity practices.
- Personal Data Protection Bill (pending): Requires careful handling of personal and sensitive data.
- ISO 27001 Certification: Encourages best practices in information security management.
Incorporating compliance into your policy reduces legal risks and strengthens trust with clients.
11. Policy Review and Updates
Information security threats evolve rapidly. Therefore, regular reviews and updates are important:
- Conduct annual policy reviews or after major incidents.
- Update the policy to reflect new technologies, regulations, and business processes.
- Communicate updates clearly to all employees and stakeholders.
Companies that neglect policy updates may face increased vulnerability to cyberattacks.
How Nurture IT Can Help
For businesses in Bangalore, partnering with Nurture IT, a leading IT solutions company in Indiranagar, can strengthen your information security framework. With years of experience supporting organizations across IT and other sectors, Nurture IT provides end-to-end solutions tailored to your company.
Here’s how we help:
- Customized Security Strategies: We assess your current systems, identify potential vulnerabilities, and design policies that protect sensitive data while fitting seamlessly into your operations.
- Advanced Security Tools: From firewalls and antivirus software to secure cloud storage and data encryption, we deploy the right technology to safeguard your information assets.
- Regulatory Guidance: Nurture IT helps businesses comply with Indian regulations such as the IT Act, CERT-In advisories, and emerging data privacy laws, keeping your practices aligned with legal requirements.
- Continuous Monitoring and Support: Our proactive monitoring of networks and systems helps detect and respond to threats in real time.
- Employee Awareness Programs: We provide workshops and training sessions to educate your staff about safe online practices, phishing attacks, and proper handling of sensitive information.
By working with Nurture IT, businesses can implement a robust information security policy while focusing on growth and operational efficiency.
Final Thoughts
A well-drafted information security policy not only minimizes risk but also builds trust among clients, employees, and business partners.
Partnering with Nurture IT in Indiranagar can help your business implement a comprehensive information security framework, leveraging advanced tools, continuous monitoring, and expert guidance. Reach out to us today!
FAQs
1. What is an information security policy?
It is a formal document outlining how a company protects, manages, and distributes its information assets.
2. Why is information security policy important for businesses?
It helps protect sensitive data, prevents financial losses, and maintains compliance with Indian regulations.
3. How can employees contribute to information security?
By following policies, attending training, recognizing threats like phishing, and reporting incidents promptly.
4. What role does an IT solutions company like Nurture IT play?
We provide customized security strategies, advanced tools, compliance guidance, monitoring, and employee awareness programs.