Common Information Security Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Today, companies of all sizes face growing threats from cybercriminals, insider risks, and accidental data leaks. Yet, despite investing in security tools, many organizations still make avoidable mistakes that leave sensitive data vulnerable. Understanding these common pitfalls and implementing practical strategies can significantly strengthen the information security posture.
Why Information Security Matters
Information security protects digital assets, confidential data, and intellectual property from unauthorized access, theft, or corruption. A breach can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, legal penalties, and regulatory non-compliance. The 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM shows just how high the financial stakes are, with the average cost of a breach now up to $4.45 million globally. Here are a few common mistakes companies can address proactively.
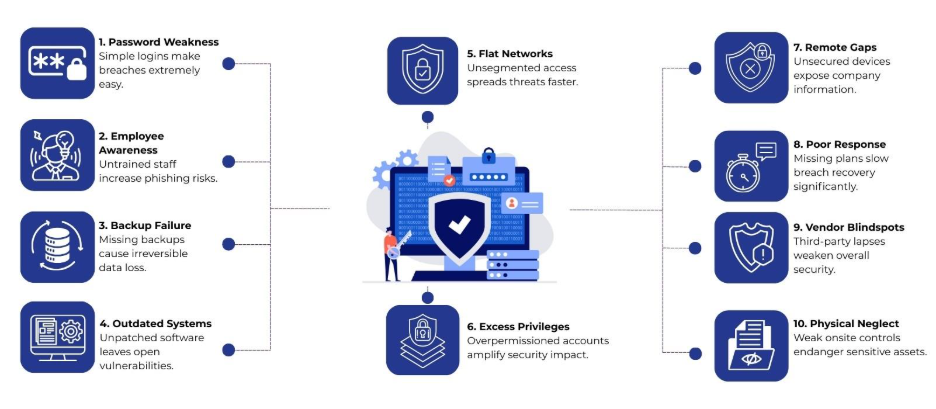
1. Weak Password Policies
The Mistake: Many companies still rely on simple or default passwords for user accounts, system logins, and administrative access. Weak passwords are easy for attackers to crack using brute force attacks or credential stuffing.
How to Avoid It
- Adopt strong password requirements that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all critical systems.
- Notify employees to use password managers to store and generate complex passwords.
2. Lack of Employee Awareness and Training
The Mistake: Employees remain one of the weakest links in information security. Without proper training, staff can fall prey to phishing emails, social engineering attacks, or unsafe browsing practices.
How to Avoid It
- Conduct regular information security awareness programs.
- Run phishing simulations to train employees on identifying malicious emails.
- Establish a clear reporting mechanism for suspicious activity.
3. Insufficient Data Backup and Recovery Plans
The Mistake: Companies often neglect regular backups or fail to test their recovery procedures. In the event of ransomware attacks, system failures, or accidental deletions, this can lead to irreversible data loss.
How to Avoid It
- Implement automated and frequent data backups for all critical systems.
- Store backups in multiple locations, including cloud as well as off-site storage.
- Periodically test backup restoration processes to confirm data integrity.
4. Outdated Software and Systems
The Mistake: Running outdated operating systems, applications, or security tools leaves vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Delaying patches and updates is a common and dangerous practice.
How to Avoid It
- Maintain a centralized system for tracking software versions and patches.
- Apply security updates promptly as they are released.
- Retire unsupported software and migrate to modern, secure solutions.
5. Poor Network Segmentation
The Mistake: Lots of organizations run on flat networks, which means devices and departments can access everything without any restrictions. This increases the risk of malware spreading quickly or internal data leaks.
How to Avoid It
- Segment networks based on function, sensitivity, or department.
- Implement access controls that restrict users to only the resources they need.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual activity.
6. Ignoring the Principle of Least Privilege
The Mistake: Giving employees or contractors excessive access rights is a common information security error. Overprivileged accounts increase the potential impact of accidental or malicious actions.
How to Avoid It
- Apply the principle of least privilege by granting only the permissions necessary for specific roles.
- Regularly audit user accounts and access levels.
- Remove access immediately when employees leave or change roles.
7. Neglecting Mobile and Remote Security
The Mistake: With the rise of remote work, unsecured mobile devices and home networks have become major targets for cyberattacks. Ignoring mobile security practices puts company data at risk.
How to Avoid It
- Require encryption and strong authentication on all mobile devices.
- Implement virtual private networks (VPNs) for secure remote access.
- Establish clear policies for using personal devices for work purposes.
8. Weak Incident Response Planning
The Mistake: Many companies lack a formal incident response plan or have outdated procedures. This slows down response times during a breach, increasing damage and recovery costs.
How to Avoid It
- Develop a documented incident response plan with defined roles and responsibilities.
- Conduct regular tabletop exercises to simulate security incidents.
- Maintain relationships with cybersecurity experts or vendors for rapid support.
9. Inadequate Vendor and Third-Party Management
The Mistake: Organizations often assume third-party vendors maintain strong security practices. This oversight can create vulnerabilities if vendors are compromised.
How to Avoid It
- Evaluate vendor security policies and certifications before engagement.
- Include security requirements in contracts with third-party providers.
- Monitor vendor access and conduct periodic audits.
10. Overlooking Physical Security
The Mistake: Focusing solely on digital security while neglecting physical safeguards is another common misstep. Unauthorized access to facilities can compromise servers, laptops, and sensitive documents.
How to Avoid It
- Implement controlled access to offices and server rooms.
- Use surveillance systems and visitor logs.
- Secure physical devices with locks or encryption.
How Nurture IT in Bangalore Protects Your Information Security
Since our office is right here in Indiranagar, Nurture IT really goes the extra mile to strengthen your information security.
Access Management: Nurture IT offers Identity Access Management (IAM) solutions to manage digital identities, assign user roles, and implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for secure access.
Our firewalls, whether physical, cloud-based, or device-specific, control network traffic, while VPN solutions provide encrypted connections for safe remote access. Active Directory services streamline authentication, access controls, and group policy management.
Data Management: We implement robust backup strategies following the 3-2-1 rule and WORM policies to protect critical data. Information Rights Management (IRM) restricts access to authorized personnel. In the event of a cyberattack, Nurture IT helps create recovery plans that restore systems and data quickly, reducing operational disruptions.
Data Protection: Advanced Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP), antivirus solutions, and USB blocking guard against malware and cyber threats. Mobile Device Management (MDM) secures corporate devices, while Data Loss Prevention (DLP) technologies monitor and prevent unauthorized data access or leaks.
With Nurture IT, organizations can strengthen digital defenses, protect valuable information, and respond swiftly to cyber threats.
Final Thoughts
Avoiding common information security mistakes requires a combination of policies, training, technology, and ongoing vigilance. Weak passwords, untrained employees, outdated systems, and poor incident response are avoidable risks that can have serious consequences. By addressing these issues proactively, companies can protect sensitive information, maintain trust with clients, and reduce the likelihood of costly breaches.
At Nurture IT, we help businesses implement robust information security strategies, from network protection to advanced data management solutions.
Get in touch with us today and take the first step toward stronger information security.
FAQs
1. What is information security and why is it important?
Information security involves protecting digital data and IT systems from unauthorized access, misuse, or theft. It safeguards sensitive information, reduces risks, and helps businesses maintain compliance.
2. What are the most common information security mistakes companies make?
Common mistakes include weak passwords, lack of employee training, outdated software, insufficient backups, overprivileged accounts, and poor incident response planning.
3. How can companies improve their information security posture?
Companies can strengthen information security by enforcing strong passwords, implementing multi-factor authentication, training employees, segmenting networks, and maintaining regular backups.
4. Why is employee awareness critical for information security?
Employees are often the first line of defense. Awareness training helps them recognize phishing attacks, avoid unsafe practices, and report suspicious activity, reducing breach risks.
5. What role do backups play in information security?
Backups protect against data loss from ransomware, system failures, or accidental deletions. Regularly tested backups allow companies to recover critical data quickly.